Arc électrique : Facteurs clé pour maintenir la sécurité – 2e partie

Quand un défaut d’arc se produit, il en résulte une explosion électrique importante. Un arc électrique libère des gaz chauds et des concentrés d’énergie rayonnante jusqu’à quatre fois la température de la surface du soleil, qui peut faire fondre le métal et causer des brûlures graves, endommager la vue et entraîner le décès. Les ondes de pression d’accompagnement peuvent endommager l’ouïe ou de la fonction cérébrale et envoyer du matériel en vrac, des outils, des machines et des débris qui volent peuvent causer d’autres blessures. Même si un jet d’arc ne blesse pas une personne, il va endommager l’équipement et provoquer des temps d’arrêt. On parle ici de 7 mesures pour prévenir l’arc.
Although the extended life of LEDs compared to other lighting solutions is beneficial, it also presents a compatibility challenge with older technology controls, especially with outdoor photocontrols. The rapid change to LED fixtures and luminaires can leave contractors, designers and distributors facing questions they cannot answer. Here are four photocontrol design solutions to minimize the effects of high inrush currents on electronic ballasts.
1. Employ a high-current rated thermal or electromechanical relay (brute force approach)
An electromechanical relay life can be shortened when switching high inrush currents that exceed the relay’s electrical ratings. With high inrush currents, significant electrical sparks can occur during switching, causing pitting and wear on the relay’s contact surface. Relays with high current ratings take these transients more effectively, as they are designed with thicker, more durable conductive materials. Electronic ballast photocontrols with high inrush currents require higher rated relays than what is suggested when considering the steady state current.
2. Implement predictive load transfer switching techniques (cost-effective approach)
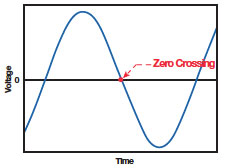
The inrush current exposure for relay contacts can be minimized with predictive load transfer switching. One technique, called zero crossing, limits the relay current by monitoring the AC supply voltage curve and timing the switching to occur as the AC voltage level passes through zero volts (See Figure 1). This effective technique extends relay contact life without relying on the rated contact current or the quality of the manufacturer, thus providing a more compact and cost-effective design.
Figure 1: Zero crossing turn-on waveform
3. Use photocontrols with solid-state switches (costlier approach)
Semiconductors such as triacs, SCRs, bipolar transistors and MOSFETs may directly switch loads. All are reliable, simple to control, and successfully handle high inrush currents. However, because of their voltage drop (‘on’ resistance), they ineffectively conduct electrical currents for an extended amount of time, generating unwanted heat. Methods to remove this heat increase the size and cost of the control.
4. Use a hybrid solid-state/relay switch design(costly approach)
The use of a hybrid semiconductor relay assisted circuit has proved effective in mitigating the heat rise issue with solid-state switching. However, costs are increased due to a higher component count. This circuit initially switches the load via the semiconductor to tolerate the inrush current, then transfers the current to a relay contact for reduced thermal operation.
Reliable photocontrols performance ratings
Contractors beware. Some manufacturers claim controls are “LED compatible,” but those terms don’t describe the actual performance of the controls over the lifetime of the LED fixture. The importance of supplying electrical contractors with reliable information on photocontrols performance motivated Intermatic to develop a comprehensive testing approach. This provides electrical contractors and distributors with explicit and tested information on the performance of the Intermatic lighting control portfolio with LED lighting to help them make informed decisions.
Source: Intermatic Incorporated, 7777 Winn Road, Spring Grove, IL 60081; 815-675-2321; www.intermatic.com/zerocross. Intermatic’s new line of electronic photocontrols for LED applications successfully utilizes zero crossing techniques to suppress inrush current impact and deliver on the extended lifespan of LED luminaires. As a result, Intermatic offers cost-effective, 8 to 12 year warrantied electronic photocontrols, while providing large inrush current carrying capacities. Lab testing shows the visible reduction of inrush current, which Intermatic has captured on video.